Resampling using Multivariate Entropy in Classification
대학원 ‘비모수통계학’ 수업에서 Short Article로 발표한 Resampling using Multivariate Entropy in Classification에 대해 올려봅니다.
-
- 주제
- Imbalanced data의 Entropy를 고려한 Resampling방법의 Classification 성능 비교
-
- 주제 설명
- Imbalanced data는 특히 2%이하의 낮은 event를 보이는 데이터로 resampling이 필수적이다. 기존의 Imbalanced data를 Resampling방법 중 Synthetic 방법은 범주형 변수에 사용하기 어렵다는 단점이 있다. Entropy가 데이터의 정보량을 담고 있으므로, Random resampling보다 Class의 Entropy을 고려한 Resampling이 더욱 좋은 효과를 보일 것이라 기대하였다. 따라서 Imbalanced data의 Classification에서 Random sampling과 Entropy를 고려한 Sampling과의 성능을 비교해보고자 한다.
1. Entropy and Empirical Entropy
\[H(X) = - \int p(x)\log p(x)\]Entropy는 event에 대한 surprise, 혹은 rareness을 담고 있다. 동전던지기를 예로 들면 앞면이 나올 확률이 0.5로 결과를 가장 알 수 없을 때의 entropy가 가장 높게 나온다.
\[\begin{gather} \widehat{ H(X) } = - \sum_{i} f_{i} \log f_{i} \\ \text{where } f_{i} \text{ is empirical frequency} \end{gather}\]- $ \text {Observed counts for each bin (i=1,… ,11)} $
| i | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| counts | 4 | 2 | 3 | 0 | 2 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 1 |
- $ \text{Empirical frequency} f_{i} $
| i | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| $freq(f_{i})$ | 0.2105 | 0.1052 | 0.1578 | 0 | 0.1052 | 0.2105 | 0 | 0 | 0.105 | 0.0526 | 0.0526 |
- $ \text{Empirical estimate of Entropy} $
Entropy를 empirical하게 추정하는 방법으로 Maximum likelihood인 $p_i=1/n$을 사용하여 histogram으로 추정하는 방법이 있다. 즉 각 bin에서 frequency에 따라 entropy가 부여되는 것이다. imbalanced dataset의 resampling시에 majority class와 minority class의 empirical entropy를 고려해준다면 두 class의 정보량이 고르게 고려되어 classification의 성능이 개선될 수 있다고 생각하였다.
2. Limitations of Resampling Methods
기존의 resampling방법 중 SMOTE는 성능이 좋다고 알려져 있다. 그러나 이는 Synthetic data를 생성하므로써 categorical variable이나 범위가 정해진 variable에서 사용하기 어렵다. 예를 들어 성별이 남(0), 여(1)일 때, 0.5로 생성된 Synthetic data는 그 의미를 알기 어렵다. 따라서 categorical variable이 존재하는 data에서 SMOTE를 사용한 oversampling보다 entropy를 고려한 sampling이 효과적일 수 있다고 가정한다. random sampling이나 SMOTE에서 borderline을 고려한 sampling보다 entropy를 활용한 sampling이 더 효과적인지 증명해보고자 한다.
3. Proposed Resampling Methodology using Entropy
X와 Y의 변수가 독립이라면 아래와 같은 joint entropy $H(X,Y)$를 얻을 수 있다.
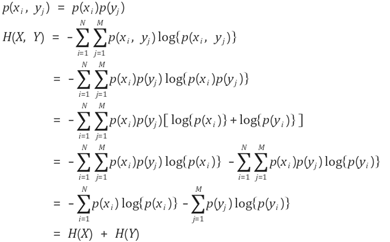
Entropy는 독립일 경우 Additive한 성질을 가진다. 이 article에서는 n개의 모든 독립변수가 독립이라는 가정 하에 Empirical entropy를 additive하게 사용하였다. 따라서 entropy 기반의 algorithm은 아래와 같다.
3.1. Algorithm 1 - Over-sampling of minority class
Step 1. Calculate Empirical entropy of majority class
\[\widehat{H_{major}} (X_1,…,X_n ) \simeq \widehat{H_{major}} (X_1) + ⋯ + \widehat{H_{major}} (X_n )\]Step 2. Over-sample with replacement of minority class and calculate $\widehat{H_{resampled}}$ until $\widehat{H_{resampled}} \simeq \widehat{H_{major}}$
# Resampled class : Sample N(Number of majority class samples) from minority class samples
k = 0
While(k =< max_iter) {
k = k+1
(H_resamp(X_1,…,X_n)) = H_resamp(X_1)+⋯+H_resamp(X_n)
If (|H_resamp-H_major|<ϵ) break
}
3.2. Algorithm 2 - Under-sampling of majority class
Step 1. Calculate Empirical entropy of minority class
\[\widehat{H_{minor}} (X_1,…,X_n ) \simeq \widehat{H_{minor}} (X_1) + ⋯ + \widehat{H_{minor}} (X_n )\]Step 2. Under-sample without replacement of minority class and calculate $\widehat{H_{resampled}}$ until $\widehat{H_{resampled}} \simeq \widehat{H_{minor}}$
# Resampled class : Sample M(Number of minority class samples) from majority class samples
k = 0
While(k =< max_iter) {
k = k+1
(H_resamp(X_1,…,X_n)) = H_resamp(X_1)+⋯+H_resamp(X_n)
If (|H_resamp-H_minor|<ϵ) break
}
4. Simulation and Results
시뮬레이션에 사용한 데이터는 3가지의 imbalanced data로 numeric과 categorical variable에 대하여 수행하였다. Binary classification만 고려했으며, 사용한 분석 방법은 Decision Tree이다. Random sampling과 SMOTE를 이번에 제안하는 entropy를 고려한 sampling 방법과 AUC로 비교하였다.
hacide dataset
X변수: 2개(numeric)
Y변수: class 1(2%), class 0(98%)
2%의 imbalanced data이며 변수간 correlation이 0.05정도로 낮은 hacide dataset으로 시뮬레이션을 수행한 결과이다.
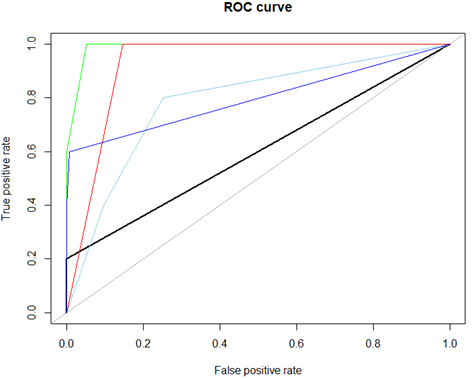
| Sampling method | AUC |
|---|---|
| non-sampling(back) | 0.600 |
| SMOTE(green) | 0.989 |
| random oversampling(orange) | 0.798 |
| random undersampling(skyblue) | 0.785 |
| oversampling using entropy(blue) | 0.798 |
| undersampling using entropy(red) | 0.927 |
undersampling using entropy(red)이 SMOTE(green)에 비견할만한 성능을 보이고 있다. 이는 98%의 다수 데이터를 2%로 줄일 때, entropy를 고려하여 효과적으로 sampling을 했음을 반증한다.
이에 반해 oversampling using entropy(blue)은 random oversampling(orange)과 같은 AUC를 보이고 있다. 이는 복원추출로 2%의 소수 데이터를 복제하면 entropy가 더 이상 오르지 않는다는 것인데 비슷한 데이터를 가지게 되기 때문이라 추측된다.
(다른 시뮬레이션 업데이트 중)
5. Discussion
데이터에서 random하게 sampling하는 방법보다 entropy를 고려하는 방법은 특히 numerical variable을 다수 가진 데이터에서 undersampling을 할 시에 효과적이다. 그러나 데이터에서 주어진 모든 변수가 독립인 것은 아니므로 additive하게 entropy를 더하는 것은 bias가 생긴다. 따라서 ‘Efficient Multivariate Entropy Estimation via K-nearest Neighbour distances’(TB Berett, 2016)에서 제안한 방법을 이용하여 보완한다면 categorical variable에서도 성능이 더 개선될 것이라 예상한다.
6. References
- ‘Efficient Multivariate Entropy Estimation via K-nearest Neighbour distances’ (TB Berett, 2016)